Is Fiber Cement Siding Cheaper Than Vinyl?
Is fiber cement siding cheaper than vinyl? That’s the million-dollar question many homeowners grapple with before starting a siding project. While vinyl often boasts a lower upfront cost, fiber cement’s superior durability and longevity can significantly impact long-term expenses. This exploration dives into the initial price differences, factoring in installation and regional variations. We’ll then compare long-term maintenance, repair costs, and even the environmental impact of each material, helping you make an informed decision that best suits your budget and priorities.
We’ll examine the lifecycle costs, considering factors like lifespan, maintenance needs, and potential repairs over two decades. Beyond the financials, we’ll also assess the aesthetic appeal, installation complexity, and the influence of siding choice on your home’s resale value. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which siding option aligns best with your needs and long-term goals.
Initial Cost Comparison
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves careful consideration of upfront costs. While vinyl often boasts a lower initial price per square foot, the long-term value proposition of fiber cement needs to be factored in. This section will break down the initial cost differences, including materials, installation, and influencing factors.
Material Costs: Fiber Cement vs. Vinyl Siding
The price difference between fiber cement and vinyl siding is significant. Vinyl typically comes in at a lower cost per square foot, while fiber cement commands a higher price due to its superior durability and longevity. However, the price range for both materials varies depending on brand, quality, and features.
| Brand | Material | Price Range/sqft | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| James Hardie | Fiber Cement | $3.00 – $8.00 | Thickness varies; some lines offer enhanced features like pre-finished colors and textures. |
| CertainTeed | Fiber Cement | $2.50 – $7.00 | Offers a range of styles and colors; thickness affects pricing. |
| LP SmartSide | Fiber Cement | $2.00 – $6.00 | Known for its engineered wood fiber composition; price varies based on features. |
| Alside | Vinyl | $1.00 – $4.00 | Wide range of styles and colors available; thickness and features impact price. |
| Mastic | Vinyl | $0.75 – $3.00 | Generally less expensive; features and color options can affect the price. |
| Royal Building Products | Vinyl | $1.50 – $5.00 | Offers higher-end vinyl options with enhanced durability and features; price reflects this. |
Installation Costs: Labor and Materials
Installation costs represent a significant portion of the overall siding project expense. Fiber cement siding generally requires more skilled labor due to its weight and installation complexity, leading to higher labor costs. Vinyl siding, being lighter and easier to install, usually results in lower labor charges. Material costs, as Artikeld above, also contribute significantly to the overall installation budget. Expect to pay anywhere from $3 to $10 per square foot for labor, depending on the siding material, complexity of the project, and regional labor rates.
Factors Influencing Initial Costs
Several factors can significantly influence the initial cost of both fiber cement and vinyl siding projects. Regional variations in labor rates and material pricing are substantial. For example, labor costs in densely populated urban areas tend to be higher than in rural areas. The installer’s experience and expertise also play a role; experienced installers may charge more but often deliver a higher quality, more efficient installation. Project complexity, including the need for extensive preparation work (like removing existing siding or addressing complex architectural details), can significantly increase both material and labor costs. Finally, the size and scope of the project directly correlate with the total cost. A larger house will naturally require more materials and labor, leading to a higher overall price.
Long-Term Costs and Maintenance

Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves considering not just the upfront cost, but also the long-term expenses associated with maintenance and eventual replacement. While vinyl might seem cheaper initially, the total cost of ownership over several decades can shift the balance significantly. Let’s delve into the details of long-term costs and maintenance for both materials.
Fiber cement and vinyl siding have vastly different lifespans and maintenance needs, influenced heavily by climate conditions. Extreme temperature fluctuations, heavy rainfall, and intense sunlight can accelerate deterioration in both materials, but to varying degrees. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Lifespan and Climate Impact
Fiber cement siding, when properly installed and maintained, boasts a remarkably long lifespan, often exceeding 50 years. However, in harsh climates with frequent freeze-thaw cycles, its lifespan might shorten slightly due to potential cracking. Coastal areas with high salinity can also impact its longevity. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, typically lasts 20-30 years, though this can be reduced significantly by intense UV exposure from prolonged sunlight and extreme temperature variations. Areas with frequent hailstorms might experience more damage to vinyl than fiber cement. For example, a house in Arizona’s desert climate might see vinyl siding fade and become brittle much faster than a similar house in a milder, humid climate like the Pacific Northwest. Conversely, a house in a northern climate experiencing significant freeze-thaw cycles might see fiber cement develop more cracks than one in a more temperate climate.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of any siding. The frequency and type of maintenance will differ between fiber cement and vinyl.
The typical maintenance tasks for each material are listed below:
- Fiber Cement: Annual cleaning with a pressure washer (low pressure to avoid damage) and occasional spot cleaning for stains. Repairs involve patching minor cracks or replacing damaged sections. Painting might be necessary every 10-15 years to maintain appearance and protect against UV degradation. Major repairs are infrequent due to the material’s durability.
- Vinyl Siding: Regular cleaning with soap and water to remove dirt and debris. Occasional power washing (low pressure) might be needed for stubborn stains. Repairs often involve replacing damaged panels, which is relatively inexpensive but can be time-consuming. Vinyl siding is prone to fading and cracking, necessitating more frequent replacements or repairs compared to fiber cement.
Projected 20-Year Cost Breakdown
Predicting exact costs is challenging, as they vary widely depending on location, labor rates, and the extent of damage. However, we can provide a general comparison based on average costs.
| Material | Initial Cost | Annual Maintenance | Major Repairs/Replacement (20 years) | Total 20-Year Cost (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | $15,000 – $25,000 | $100 – $200 | $1,000 – $3,000 | $16,200 – $28,400 |
| Vinyl | $8,000 – $15,000 | $50 – $100 | $2,000 – $6,000 | $10,200 – $21,200 |
Note: These are estimates and actual costs may vary. The major repair/replacement costs assume some level of damage or wear and tear over 20 years. Labor costs are included in these estimates.
Material Properties and Durability

Fiber cement and vinyl siding offer distinct material properties impacting their durability and longevity. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision about which siding best suits your needs and budget. We’ll explore their resistance to damage, fire performance, and environmental impact.
Fiber cement siding, a composite material made of cement, cellulose fibers, and sand, boasts superior strength and durability compared to vinyl. Its inherent density makes it highly resistant to impacts, dents, and scratches, far exceeding the resilience of vinyl. It also stands up well against harsh weather conditions, including strong winds, heavy rain, and extreme temperatures, showing minimal expansion or contraction. Vinyl, being a plastic, is more susceptible to damage from impacts and can become brittle in extreme cold or warped in intense heat. While often less expensive initially, this susceptibility to damage can lead to higher long-term replacement costs.
Impact, Weather, and Pest Resistance, Is fiber cement siding cheaper than vinyl?
Fiber cement’s robust nature provides excellent resistance to impacts from hail, flying debris, or accidental bumps. Its non-porous surface prevents moisture absorption, minimizing the risk of rot, mildew, and water damage. Furthermore, fiber cement is naturally resistant to insect infestation, unlike vinyl siding which can sometimes attract pests like termites if it becomes damaged. Vinyl siding, while relatively resistant to moisture in its undamaged state, is more easily damaged and susceptible to warping or cracking under impact, potentially creating entry points for pests and moisture.
Fire Resistance
Fire resistance is a critical safety consideration. Fiber cement siding is non-combustible and carries a Class A fire rating, the highest achievable. This means it resists ignition and offers superior protection against fire spread. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is flammable and will melt and burn in a fire, potentially contributing to the spread of flames. While treated to slow burning, it’s not comparable to the fire-resistant properties of fiber cement.
Environmental Impact
The environmental footprint of siding materials should be considered throughout their lifecycle – from manufacturing and installation to eventual disposal.
| Factor | Fiber Cement | Vinyl | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Higher energy consumption due to cement production; potential for dust and air emissions. | Relies on petroleum-based resources; releases greenhouse gases during production. | Both processes have environmental impacts; the specific impact varies depending on manufacturing processes and energy sources. |
| Installation | Requires more specialized tools and potentially more skilled labor. | Generally easier and faster to install. | Installation impacts are mostly related to labor and transportation. |
| Disposal | Can be recycled or used as landfill fill, though recycling infrastructure may be limited. | Often ends up in landfills; recycling options are limited and not widely available. | Both materials pose disposal challenges; increased recycling infrastructure could significantly reduce the environmental burden. |
| Durability & Longevity | Longer lifespan reduces the frequency of replacement and associated waste. | Shorter lifespan leading to more frequent replacements and increased waste generation. | Longevity directly impacts the overall environmental impact over the siding’s lifetime. |
Aesthetic Considerations
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding often comes down to personal preference, as both offer a wide range of aesthetic options, but their appearances and how they age differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that complements your home’s style and enhances its curb appeal.
Fiber cement and vinyl siding each provide distinct aesthetic qualities that impact a home’s overall look. The initial visual appeal, as well as how the siding ages over time, are key considerations.
Color and Texture Variety
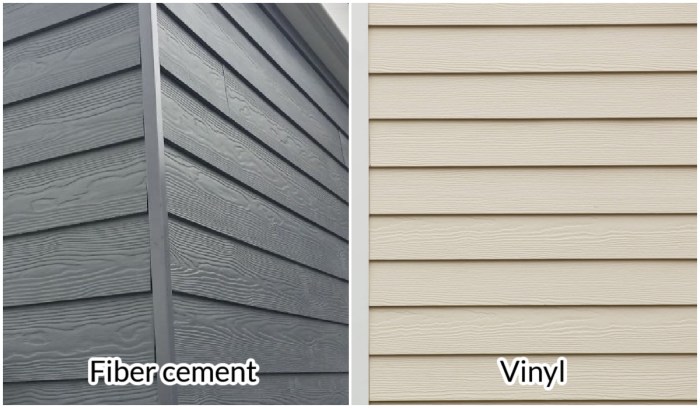
Both fiber cement and vinyl siding offer a wide array of colors. Vinyl typically boasts a broader selection of colors and finishes, often including more vibrant and unusual shades. Fiber cement, while offering a solid range of colors, might present fewer options, especially in highly specialized or trendy hues. However, fiber cement excels in texture. It can convincingly mimic the look of wood clapboard, shingle, or even stone, offering a more substantial and natural appearance than vinyl. Vinyl siding, while improving, often shows a more uniform, sometimes slightly plastic-like texture. High-end vinyl siding is making strides in mimicking wood grain textures, but fiber cement remains superior in this aspect.
Appearance Over Time
Vinyl siding is known for its relatively low maintenance, but it can be prone to fading and discoloration over extended sun exposure. The intensity of fading depends on the pigment quality and UV stabilizers used in the manufacturing process. While some high-quality vinyl sidings are designed for better UV resistance, fading remains a possibility. In contrast, fiber cement siding is more resistant to fading and discoloration. Its inorganic composition makes it less susceptible to the effects of sunlight. However, prolonged exposure to harsh weather can still lead to some subtle changes in color over many years, though typically less noticeable than with vinyl.
Architectural Style Suitability
Fiber cement’s versatility allows it to complement a wide range of architectural styles. Its ability to mimic natural materials makes it particularly suitable for homes with traditional, craftsman, or colonial designs. The realistic textures of wood shake or clapboard siding, achievable with fiber cement, add a touch of elegance and authenticity to these styles. Vinyl siding, with its wider color palette and easier installation, is often used in more contemporary or modern homes, where a clean, streamlined look is desired. However, its use in mimicking traditional styles can sometimes appear less authentic than fiber cement. For instance, a Victorian home clad in vinyl might lack the depth and texture of fiber cement, resulting in a less refined aesthetic.
Installation Process and Timelines

Installing siding, whether it’s fiber cement or vinyl, is a significant undertaking that impacts both the project’s timeline and overall cost. The processes differ in complexity and required skill levels, leading to variations in labor costs and potential delays. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate budgeting and realistic scheduling.
Fiber cement and vinyl siding installation share some similarities, such as the need for proper preparation of the house’s exterior walls. However, the materials themselves and the tools required for installation differ significantly, leading to varied installation times and potential challenges. The size and complexity of the house also play a role in the overall timeframe.
Fiber Cement Siding Installation
Fiber cement siding installation is generally considered more complex and time-consuming than vinyl siding. It requires more specialized tools and a higher level of expertise due to the material’s weight and fragility. The process typically involves precise cutting, careful handling to avoid damage, and attention to detail during installation to ensure a watertight seal. Experienced installers are usually necessary to ensure a professional finish and prevent costly mistakes. For a standard-sized house, installation can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on factors like the house’s design and the installer’s efficiency.
Vinyl Siding Installation
Vinyl siding installation is comparatively simpler and faster. The lighter weight of the material makes handling easier, and the installation process often involves less precise cutting. While expertise is still beneficial, the relative ease of installation means that less experienced installers might be able to handle the job, potentially lowering labor costs. However, cutting corners can lead to problems with water infiltration and aesthetic imperfections. For a standard-sized house, vinyl siding installation can typically be completed within a week or less by a skilled team.
Potential Installation Challenges and Cost Impacts
Several challenges can impact the installation process and drive up costs for both fiber cement and vinyl siding. For fiber cement, the material’s weight and fragility increase the risk of damage during handling and installation, potentially requiring replacement of damaged pieces. The need for precise cuts and careful sealing can also lead to increased labor costs if the installer lacks experience. Unexpected issues, such as rotted sheathing or uneven wall surfaces, can further complicate the installation and extend the timeline.
Vinyl siding presents fewer challenges, but improper installation can lead to problems such as gaps, buckling, or warping. These issues might necessitate partial or full removal and reinstallation, significantly increasing the project cost. Extreme weather conditions can also impact installation timelines, causing delays and potentially leading to additional labor charges. For example, a particularly hot and sunny day could make working with vinyl difficult, requiring breaks and slowing down the overall process. Conversely, rain can halt the process completely.
Resale Value Impact
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding can significantly impact your home’s resale value. Buyers often associate different materials with varying levels of quality, durability, and maintenance requirements, directly influencing their purchasing decisions and the price they’re willing to pay. Understanding these perceptions is crucial for homeowners considering a siding upgrade.
The perceived durability and longevity of each material heavily influence buyer preferences. Fiber cement, known for its strength and resistance to damage from weather and pests, often commands a higher resale value. Conversely, while vinyl siding is more affordable upfront, its susceptibility to damage from impact and its shorter lifespan can negatively affect a home’s perceived value. This difference in perceived longevity translates to different buyer perceptions and willingness to pay a premium.
Fiber Cement’s Positive Impact on Resale Value
Fiber cement siding’s superior durability and resistance to the elements translate to lower long-term maintenance costs for homeowners. This is a significant selling point for buyers, who often factor in the cost of future repairs and replacements when making purchasing decisions. A home with fiber cement siding projects an image of quality and low-maintenance living, potentially attracting buyers willing to pay more. Appraisers may also assign a higher value to homes with this type of siding due to its inherent longevity and the reduced risk of needing costly repairs shortly. For example, a recent appraisal report in a similar neighborhood showed a 2-3% increase in value for homes with fiber cement compared to those with vinyl siding, all other factors being equal.
Vinyl Siding’s Impact on Resale Value
While vinyl siding’s initial affordability is attractive, its shorter lifespan and susceptibility to damage can negatively affect a home’s resale value over time. The need for more frequent repairs or replacements can be a deterrent to potential buyers, especially those seeking a low-maintenance home. The perception of lower quality compared to fiber cement can also lead to a lower appraisal value. While it may not drastically reduce resale value, it’s unlikely to add significant value to a property in the same way that fiber cement siding might. Consider a scenario where two identical homes are for sale, one with vinyl and the other with fiber cement. The fiber cement-sided home is likely to receive more offers and potentially sell for a higher price.
Market Data and Expert Opinions
Several real estate market analyses suggest a correlation between the type of siding and a home’s sale price. While the exact figures vary depending on location and market conditions, studies consistently show that homes with high-quality, durable siding, such as fiber cement, tend to sell for a higher price than those with vinyl siding. Furthermore, real estate experts often advise homeowners to consider the long-term impact on resale value when choosing exterior materials. They highlight that investing in durable and aesthetically pleasing siding, even if it means a higher upfront cost, can pay off handsomely when it comes time to sell the property. This advice often emphasizes the importance of considering the return on investment, factoring in the potential increase in sale price against the initial investment.
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the “cheaper” siding depends entirely on your perspective and long-term planning. Vinyl offers an immediate cost advantage, but fiber cement’s resilience and longevity often translate to lower overall costs over its extended lifespan. Weighing the initial investment against future maintenance, repairs, and potential resale value increases is crucial. Consider your budget, climate, desired aesthetic, and your home’s overall value when making your final decision. A well-informed choice ensures a beautiful and durable exterior that serves you for years to come.
Top FAQs: Is Fiber Cement Siding Cheaper Than Vinyl
What about insurance costs? Does siding type affect premiums?
While not always a direct factor, some insurance companies might offer slight discounts for homes with more fire-resistant siding like fiber cement.
Can I mix and match fiber cement and vinyl siding?
It’s technically possible, but it’s generally not recommended due to aesthetic inconsistencies and potential challenges in matching textures and colors.
How does the climate affect the lifespan of each siding?
Harsh climates with extreme temperature fluctuations or frequent storms can impact both materials, but fiber cement tends to hold up better in the long run.
Are there any government incentives or rebates for eco-friendly siding?
Some regions offer tax credits or rebates for energy-efficient home improvements, which may sometimes include certain siding types. Check your local government’s website for details.