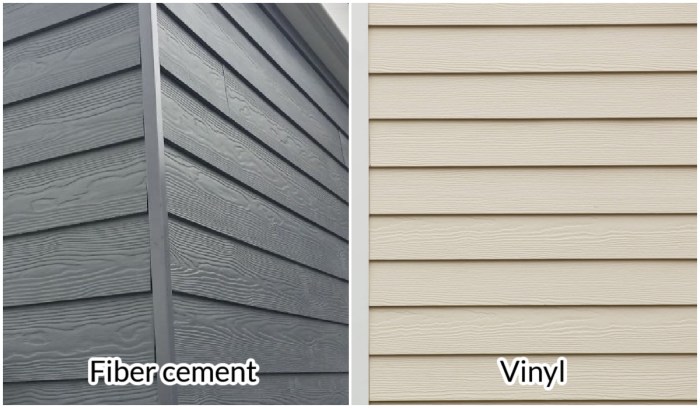
Fiber Cement Siding vs Vinyl Siding A Homeowners Guide
Fiber cement siding vs vinyl siding: Choosing the right exterior cladding for your home is a big decision, impacting both aesthetics and longevity. This guide dives into a head-to-head comparison, exploring the manufacturing processes, durability, maintenance needs, environmental impact, installation complexities, and cost considerations of each material. We’ll help you weigh the pros and cons to make an informed choice that best suits your needs and budget.
From initial costs and long-term maintenance to environmental impact and energy efficiency, we’ll examine every aspect, providing a clear understanding of the key differences between fiber cement and vinyl siding. By the end, you’ll be equipped to confidently select the perfect siding for your home, ensuring a beautiful and durable exterior for years to come.
Initial Comparison

Source: garbatibuilders.com
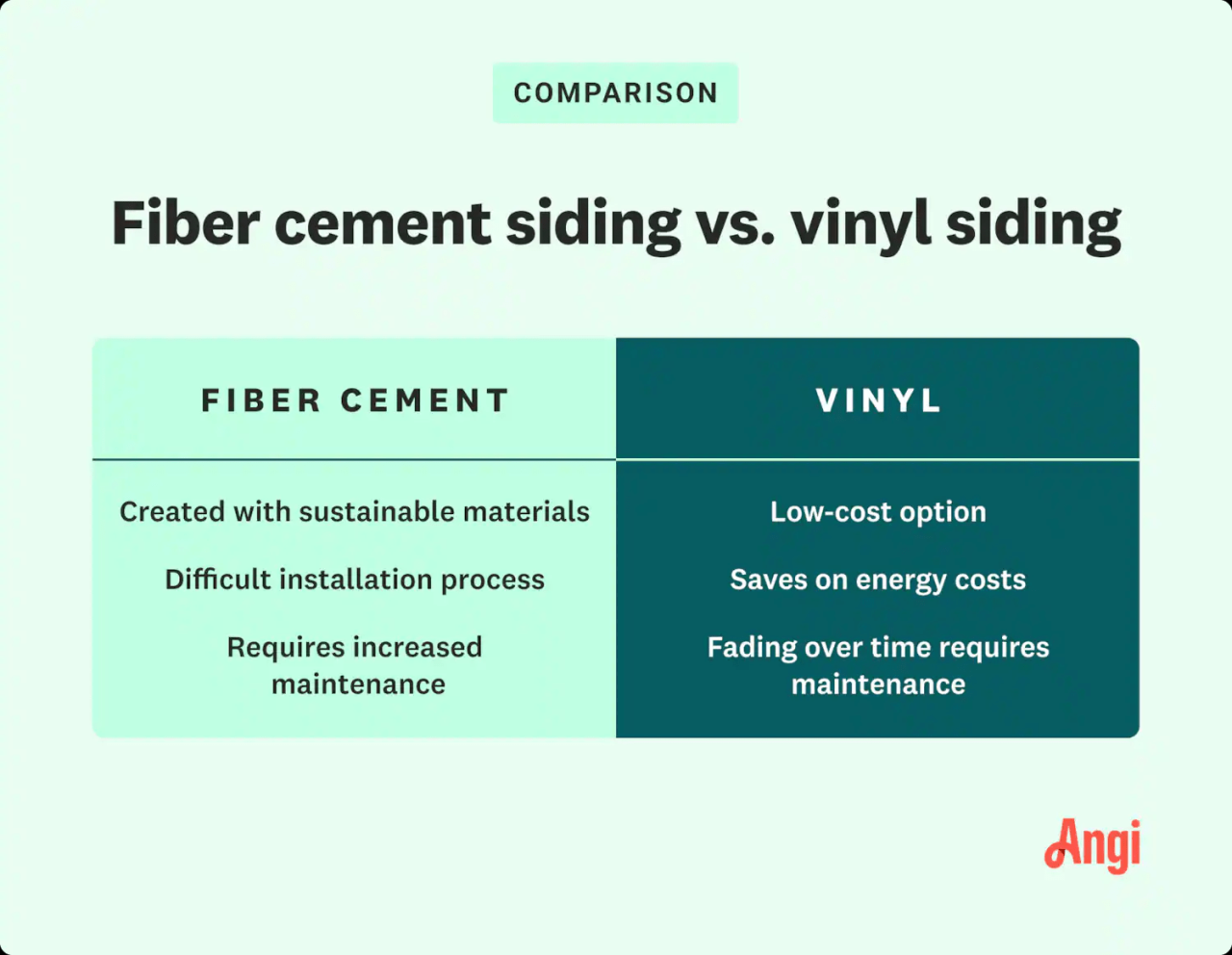
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding is a big decision for any homeowner. Both offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the core differences will help you make an informed choice that best suits your needs and budget. This section will delve into a direct comparison of these two popular siding materials.
Manufacturing Processes
Fiber cement siding is a composite material, manufactured by combining Portland cement, cellulose fibers (often wood pulp), and silica sand. This mixture is then formed into panels under high pressure and cured in a kiln, resulting in a durable and relatively fire-resistant product. In contrast, vinyl siding is produced through an extrusion process. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin, along with various additives for color, impact resistance, and UV protection, is melted and then forced through a die to create the desired shape and profile. This process allows for a wide variety of styles and colors, but the final product is less robust than fiber cement.
Lifespan Comparison
Fiber cement siding boasts a significantly longer lifespan than vinyl siding. With proper installation and maintenance, fiber cement siding can easily last 50 years or more, sometimes even exceeding 80 years. Vinyl siding, while durable, typically lasts between 20 and 40 years, depending on the quality of the material and exposure to harsh weather conditions. The longer lifespan of fiber cement often translates to lower long-term costs, despite a higher initial investment.
Aesthetic Differences
Three key aesthetic differences distinguish fiber cement and vinyl siding. First, fiber cement offers a more authentic wood-like texture and appearance, providing a natural look that’s difficult to replicate with vinyl. Second, fiber cement siding is available in a wider range of colors and finishes, allowing for greater customization. While vinyl siding also offers various colors, they can sometimes appear less nuanced and more uniform. Finally, fiber cement tends to have a more substantial and less plastic-like appearance than vinyl. This adds to its perceived higher quality and premium look.
Initial Material Cost Comparison
| Siding Type | Cost per Square Foot (USD – Estimate) | Factors Affecting Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | $3.00 – $8.00 | Thickness, texture, color, brand | Prices can vary significantly based on specific product features. |
| Vinyl | $1.00 – $4.00 | Style, color, thickness, manufacturer | Lower-end vinyl can be significantly cheaper, but might not last as long. |
Maintenance and Durability

Source: sunshinecontractingcorp.com
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves considering long-term maintenance and how well each material withstands the test of time and the elements. Both offer decent lifespans, but their maintenance needs and durability differ significantly. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision based on your budget and lifestyle.
Over ten years, the maintenance requirements for these siding types diverge considerably. Vinyl siding generally requires minimal upkeep. Occasional washing with a hose and mild detergent is usually sufficient to remove dirt and grime. Fiber cement, while more durable, needs more attention. Regular cleaning is recommended, but you might also need to address minor repairs like caulking or repainting more frequently than with vinyl.
Maintenance Requirements Over 10 Years
Vinyl siding’s low-maintenance nature translates to significant cost savings over a decade. You might spend a few hours a year cleaning it, perhaps investing in a pressure washer for more thorough cleaning every few years. In contrast, fiber cement siding, while initially more expensive, could require repainting every 5-7 years depending on climate and sun exposure, adding to the overall maintenance cost. This cost could include professional painting services, increasing the expense considerably. Regular inspection for cracks and damage is also crucial for both types, but repairs are typically simpler and less costly for vinyl.
Impact Resistance
Fiber cement siding boasts superior impact resistance compared to vinyl. It can better withstand the battering of hail, falling branches, or even accidental impacts from lawn equipment. While vinyl siding can dent or crack under similar impacts, fiber cement tends to only suffer superficial damage, often requiring only minor repairs. Imagine a severe hailstorm; fiber cement would likely show only small chips, while vinyl could sustain numerous dents and cracks requiring more extensive repair or replacement.
Susceptibility to Fading and Discoloration
Both fiber cement and vinyl siding are susceptible to fading and discoloration from prolonged sun exposure, though the extent varies. Vinyl siding is known to fade more quickly than fiber cement, especially darker colors. UV stabilizers are added to vinyl to mitigate this, but over a decade, color loss is still a possibility. Fiber cement, being a composite material, generally holds its color better, although repainting every 5-7 years (as mentioned previously) is often necessary to maintain its original appearance and protect it from further weathering.
Common Repair Methods
Repairing each siding type involves different techniques and materials.
- Vinyl Siding: Minor dents can sometimes be popped back out with a putty knife. Cracks may require patching with vinyl caulk or replacing damaged panels. Larger areas of damage usually necessitate replacing entire sections.
- Fiber Cement Siding: Minor chips and cracks can often be repaired with patching compounds designed for fiber cement. More significant damage might require replacing individual panels, which can be more labor-intensive and costly due to the material’s weight and the need for precise cutting and fitting.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves considering more than just aesthetics and cost; the environmental impact of each material plays a significant role in the long-term sustainability of your home. Both have pros and cons regarding manufacturing, lifespan, and end-of-life disposal. Let’s delve into the specifics to help you make an informed decision.
The environmental footprint of building materials is increasingly important to homeowners. Factors like energy consumption during manufacturing, the use of raw materials, and the potential for recycling all contribute to a material’s overall sustainability. Understanding these factors for fiber cement and vinyl siding allows for a more comprehensive comparison.
Manufacturing Processes and Resource Consumption
Fiber cement siding’s manufacturing process involves combining cement, cellulose fibers (often recycled wood pulp), and other additives. This process is energy-intensive, requiring high temperatures for curing. However, the raw materials are relatively abundant and, in the case of cellulose fibers, can utilize recycled content. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is primarily made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a plastic derived from petroleum. The production of PVC is also energy-intensive and relies on a non-renewable resource. Furthermore, the manufacturing process often involves the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can contribute to air pollution.
Recyclability and Disposal Options
Fiber cement siding is not readily recyclable in most areas. Disposal usually involves sending it to landfills. While some components might be reclaimed for other uses, this is not a widespread practice. Vinyl siding also presents challenges for recycling. While some specialized recycling programs exist, they are not widely available. Landfilling is the most common disposal method for vinyl siding, contributing to plastic waste accumulation in landfills. Both materials, if not properly disposed of, can pose environmental risks.
Long-Term Sustainability
The long lifespan of fiber cement siding (50+ years) contributes to its overall sustainability. While its manufacturing process has a higher initial environmental impact, the extended lifespan reduces the frequency of replacement, minimizing the need for ongoing material production. Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years, meaning more frequent replacements are needed, leading to a larger cumulative environmental impact over time. The extended lifespan of fiber cement, therefore, offsets its initial higher impact in the long run, especially when considering the continuous use of petroleum in vinyl production.
Environmental Comparison Table
| Feature | Fiber Cement Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Energy-intensive; uses cement, cellulose fibers (often recycled), and additives. | Energy-intensive; uses PVC derived from petroleum; releases VOCs during manufacturing. |
| Raw Materials | Relatively abundant; potential for recycled content (cellulose fibers). | Relies on non-renewable petroleum resources. |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options; primarily landfilled. | Limited recycling options; primarily landfilled. |
| Lifespan | 50+ years | 20-30 years |
| Overall Environmental Impact | Higher initial impact, but lower cumulative impact due to longer lifespan. | Lower initial impact, but higher cumulative impact due to shorter lifespan and reliance on petroleum. |
Installation and Cost Considerations

Source: factorydirectsiding.com
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves careful consideration of installation complexity and overall cost. Both materials offer distinct advantages and disadvantages in these areas, impacting the final project budget and timeline. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Installation complexity significantly impacts the overall project cost. Fiber cement siding, due to its weight and the need for precise cutting and fastening, generally requires more skilled labor and time compared to vinyl siding. Vinyl, being lighter and easier to manipulate, is often a quicker and less labor-intensive installation.
Installation Process Comparison
The following table Artikels the key steps involved in installing both fiber cement and vinyl siding. Note that these are simplified representations and the actual process may vary depending on specific project details and site conditions.
| Step | Fiber Cement Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Sheathing inspection, moisture barrier installation, careful measurement and marking of starter courses. | Sheathing inspection, moisture barrier installation, basic measurement and marking. |
| Installation of Starter Strips/J-Channel | Precise installation to ensure a straight and level starting point. Requires careful attention to detail. | Relatively straightforward installation; less critical to overall alignment. |
| Siding Installation | Requires specialized tools for cutting and fastening. Precise alignment and fastening are crucial to prevent cracking. | Easy to cut and install; interlocking design simplifies the process. |
| Finishing | Caulk application, trim installation, and careful attention to sealing around windows and doors. | Relatively simple finishing; less caulking required. |
Cost Breakdown of Professional Installation
The cost of professional siding installation varies considerably based on several factors, including the size of the house, the complexity of the project (e.g., numerous corners, windows, and dormers), the chosen materials, and regional labor rates. As a general guideline, let’s consider a hypothetical 1500 sq ft house.
For fiber cement siding, the material cost might range from $8,000 to $15,000, while labor costs could add another $7,000 to $12,000. This brings the total cost to somewhere between $15,000 and $27,000. Higher-end fiber cement brands and intricate designs will naturally increase this range.
Vinyl siding installation, on the other hand, is typically less expensive. Materials might cost between $5,000 and $10,000, with labor costs ranging from $4,000 to $8,000. The total cost for vinyl siding would likely fall between $9,000 and $18,000.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Several factors beyond the basic material and labor costs contribute to the final price. Labor rates vary significantly by region; areas with higher costs of living generally have higher labor rates. The complexity of the house’s design, including the number of corners, windows, and other architectural details, directly impacts the time and labor required. Premium brands of both fiber cement and vinyl siding command higher prices. Finally, permits and inspections add to the overall cost. Unexpected issues discovered during the installation process (like rotted sheathing) can also lead to additional expenses. For example, a project in a high-cost area with a complex house design might see significantly higher costs than a similar project in a lower-cost area with a simpler design.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding involves considering more than just aesthetics; energy efficiency plays a crucial role in long-term homeownership costs and environmental impact. Both materials offer varying degrees of insulation, impacting your heating and cooling bills. Let’s delve into the specifics of their thermal performance and the potential energy savings they offer.
Fiber cement and vinyl siding differ significantly in their thermal properties. Fiber cement, being a composite material, possesses a higher density and mass than vinyl. This density contributes to its superior ability to resist heat transfer, meaning it helps maintain a more stable indoor temperature. Vinyl, on the other hand, is a lightweight plastic material with inherently lower thermal resistance. While some vinyl siding products incorporate insulating foam backing, this doesn’t always negate the fundamental difference in thermal mass between the two materials.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Imagine two identical houses, one sided with fiber cement and the other with vinyl. A visual representation of their thermal performance could be depicted as two bars. The bar representing the fiber cement-sided house would be significantly thicker and darker, illustrating its higher thermal mass and resistance to heat transfer. The vinyl-sided house’s bar would be thinner and lighter, representing its lower thermal resistance and greater susceptibility to temperature fluctuations. This difference in thermal performance directly translates to energy consumption.
Energy Savings Over 20 Years
Predicting precise energy savings requires considering several factors such as climate, home size, insulation levels in walls and attics, and heating/cooling system efficiency. However, we can illustrate potential differences. Let’s assume a typical home in a moderate climate with average energy costs. A fiber cement-sided home might see an average annual energy savings of around $200-$300 compared to a vinyl-sided home over the 20 years. This translates to a potential total savings of $4000-$6000. This is a rough estimate; actual savings could be higher or lower depending on the factors mentioned earlier. For example, a home in a much colder climate could see significantly greater savings with fiber cement due to its superior insulation properties, potentially exceeding the estimated range. Conversely, a home in a mild climate might see a smaller difference.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
The impact on a home’s overall energy efficiency is significant. Fiber cement siding contributes to a more thermally stable home environment, reducing the strain on heating and cooling systems. This leads to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions. While vinyl siding offers some level of insulation, its lower thermal mass means that your HVAC system will likely work harder to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, especially in extreme weather conditions. This increased energy usage translates to higher utility bills and a larger carbon footprint.
Resistance to Weather and Pests
Choosing between fiber cement and vinyl siding often comes down to understanding how each material handles the elements and potential pests. Both offer protection for your home, but their strengths and weaknesses differ significantly when facing harsh weather and unwanted critters. This section details how each material performs under various conditions.
Fiber Cement and Vinyl Siding: Weather Resistance
Fiber cement siding boasts superior resistance to extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV degradation compared to vinyl. Its cement composition allows it to withstand significant temperature fluctuations without warping, cracking, or fading. Vinyl, while relatively weather-resistant, can become brittle in extreme cold, potentially cracking, and may soften and sag in intense heat. Prolonged exposure to moisture can also lead to issues with vinyl, such as mildew growth. Fiber cement, on the other hand, is highly resistant to moisture and fungal growth, making it an excellent choice in humid climates.
Pest Infestation Susceptibility, Fiber cement siding vs vinyl siding
Fiber cement’s dense, non-organic composition makes it highly resistant to insect infestation, including termites. The material offers no nutritional value to these pests, deterring them from causing damage. Vinyl siding, being a plastic polymer, is also generally resistant to insect damage, though certain types of insects might occasionally cause minor surface scratches. However, it’s crucial to note that neither material prevents pest damage to the underlying structure of the home. Proper pest control measures are still essential regardless of the siding material used.
Performance in Hurricane-Prone Areas and Extreme Weather
In areas prone to hurricanes or high winds, fiber cement siding’s superior strength is a significant advantage. Its robust nature helps it withstand high winds and impact from debris, minimizing damage during severe weather events. Vinyl siding, while relatively lightweight, can be easily damaged by high winds and flying debris, potentially leading to significant damage and requiring extensive repairs. The impact resistance of fiber cement offers greater protection to the underlying structure of the house.
Long-Term Performance in Different Climates
Fiber cement siding demonstrates excellent long-term performance across a wide range of climates. Its durability and resistance to moisture make it a suitable choice for both hot, humid environments and cold, snowy regions. While vinyl siding can also last for many years, its performance can degrade more quickly in extreme climates. For instance, prolonged exposure to intense UV radiation in sunny regions can lead to fading and embrittlement of vinyl, while repeated freeze-thaw cycles in colder areas can cause cracking. The long-term cost-effectiveness of fiber cement, due to its greater longevity, often outweighs the higher initial investment.
Conclusion
Source: angi.com
Ultimately, the “best” siding – fiber cement or vinyl – depends entirely on your priorities. Fiber cement offers superior durability, weather resistance, and a more natural look, but comes with a higher initial cost and more complex installation. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is budget-friendly and easy to install, but may not last as long or withstand harsh weather as effectively. Carefully consider your budget, climate, aesthetic preferences, and long-term maintenance expectations before making your final decision. This detailed comparison should provide the information you need to make the right choice for your home.
Question & Answer Hub: Fiber Cement Siding Vs Vinyl Siding
Can I install fiber cement or vinyl siding myself?
While vinyl siding is often DIY-friendly for those with some construction experience, fiber cement siding is generally best left to professionals due to its weight and more complex installation process.
How does each siding type handle insect infestations?
Fiber cement is naturally resistant to insect damage, while vinyl siding can be susceptible to certain pests, particularly if it’s damaged. Regular inspection is recommended for both.
What about insurance considerations?
Some insurance companies may offer discounts for homes with fiber cement siding due to its superior durability and fire resistance. Check with your provider for specific details.
Which siding is better for coastal areas?
Fiber cement generally performs better in coastal areas due to its superior resistance to moisture and salt damage compared to vinyl siding.
What are the warranty options for each?
Both fiber cement and vinyl siding manufacturers offer warranties, but the length and coverage can vary significantly. Always check the specifics before purchasing.




